You’ve probably seen the word Blockchain everywhere in crypto conversations, tech spaces or across social media. Yet for many people the concept still feels confusing, technical or too advanced.
But here’s the truth, blockchain is simply a new, smarter way of storing information. It’s open, secure, transparent and built for a future where trust is created by technology not middlemen. In this guide we break it all down in the simplest most human way possible.
What Exactly Is Blockchain?
Imagine a notebook that everyone can see, everyone can write on, and no one can secretly erase.That’s what a blockchain is.
Once information goes into the blockchain:
✓ It cannot be changed
✓ It cannot be deleted
✓ It cannot be hidden
This creates trust, fairness and transparency automatically.
Why Blockchain Matters
The world runs on trust.
We trust banks, governments, schools and institutions to keep our records safe. But the reality is:
✓ Data gets hacked
✓ Systems fail
✓ Records get manipulated
✓ People get excluded
Blockchain removes this risk by making data:
✓ open
✓ verifiable
✓ secure
✓ honest by design.
This is why blockchain feels less like a technology and more like a movement toward digital fairness and empowerment.
How Blockchain Works (Step-by-Step)
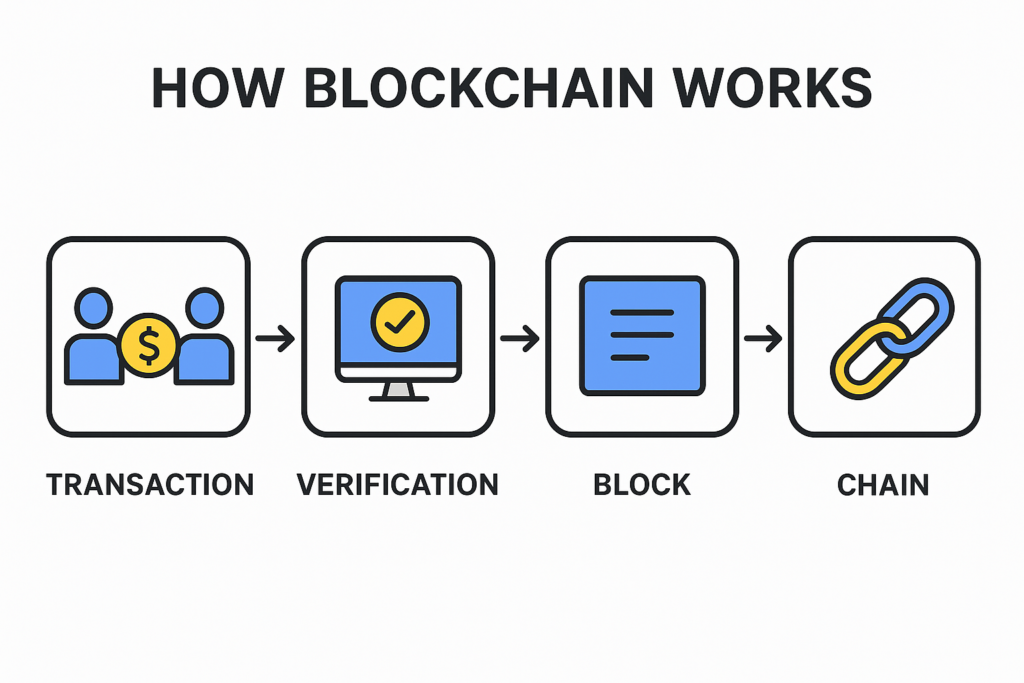
➛ A transaction happens sending crypto, updating a record, signing a digital contract.
➛ Network of computers (nodes) verify it
➛ The transaction is added to a block
➛ The block is sealed and added to the chain
➛ The chain becomes the permanent public history
Simple. Transparent. Secure.
Features and Characteristics of Blockchain
➛ Decentralization
No single company or authority controls the system.
➛ Transparency
Everyone can view the transaction history.
➛ Immutability
Data cannot be edited after it is added.
➛ Security
Protected by cryptography and distributed storage.
➛ Trustless Environment
You don’t have to trust people — the system enforces honesty.
➛ Efficiency
Faster transactions without middlemen.
➛ Distributed Ledger
Data exists everywhere, reducing risk of failure.
➛ Smart Contracts
Self-executing agreements with no need for third-party approval.
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain
▼ Finance: Fast and cheap cross-border payments
▼ Education: Secure, verifiable certificates
▼ Healthcare: Safer patient records
▼ Supply Chain: Track products from origin to destination
▼ Government: Transparent voting and public records
▼ Media & Art: Digital ownership and creator protection
▼ Web3 & DeFi: New financial systems based on code
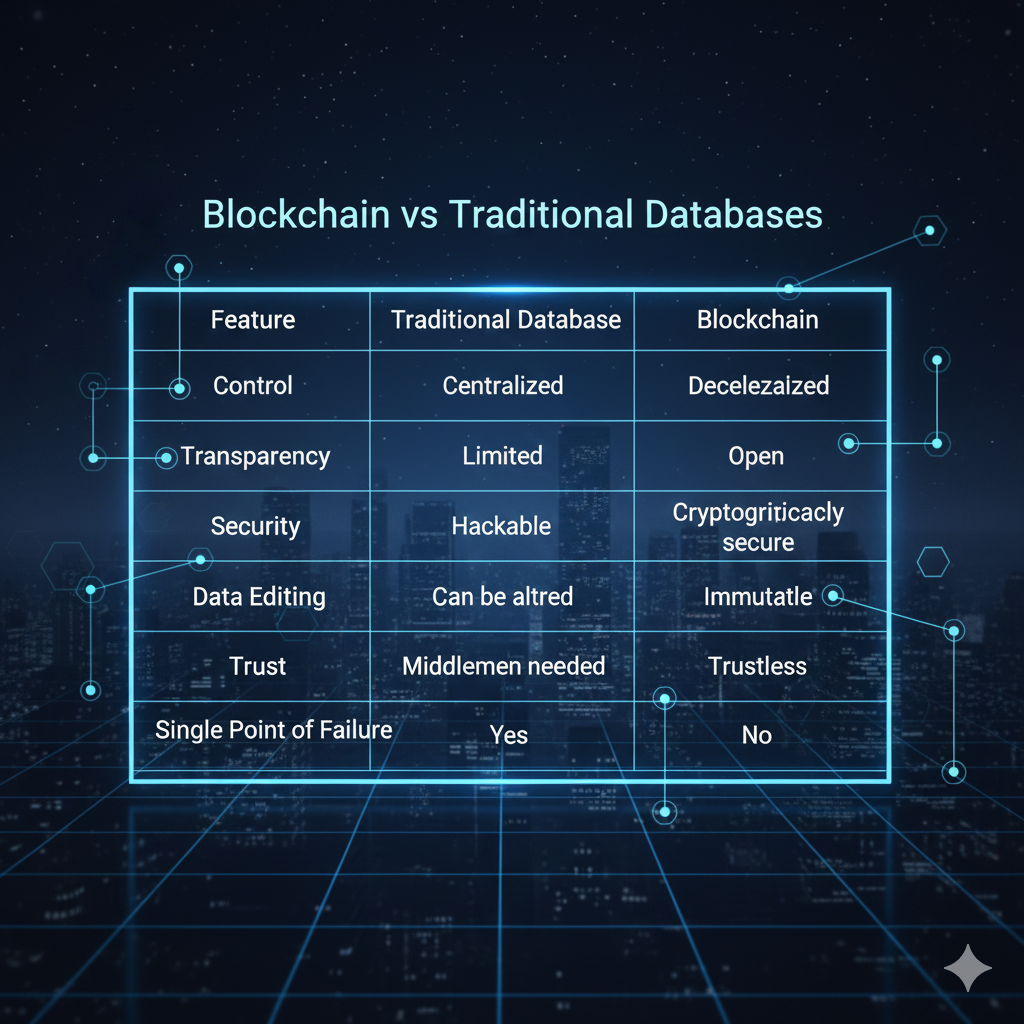
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
Why Blockchain Is Critical for Emerging Markets
Blockchain solves real problems affecting millions of people:
⪼ financial inequality
⪼ corruption
⪼ document fraud
⪼ lack of financial access
⪼ identity issues
⪼ unverified records
It empowers communities with:
⪼ borderless money
⪼ transparent systems
⪼ digital ownership
⪼ new income opportunities
⪼ global access
For emerging markets, blockchain isn’t just tech. It’s a tool for economic freedom and digital inclusion.
Conclusion
The Future Is Built on Blockchain
Blockchain marks a shift from Web2 centralized control to Web3 decentralized ownership.
Understanding it today means:
⪼ preparing for future jobs
⪼ participating in digital economies
⪼ unlocking new opportunities in finance, business and technology.
Whether you’re a creator, business owner, student or investor blockchain offers something powerful, a world where you truly own your data, your money and your digital identity.




